Section 21.1 factors that affect climate answer key – Unveiling the intricate factors that shape our planet’s climate, this exploration delves into Section 21.1, providing a thorough understanding of the forces that govern our environment. From natural phenomena to human influences, we embark on a journey to unravel the complex mechanisms driving climate patterns.
Understanding the factors that affect climate is crucial for navigating the challenges posed by environmental change. This guide will illuminate the interplay between natural and human-induced influences, empowering readers with knowledge to mitigate their impact and adapt to the evolving climate landscape.
Overview of Section 21.1 Factors that Affect Climate
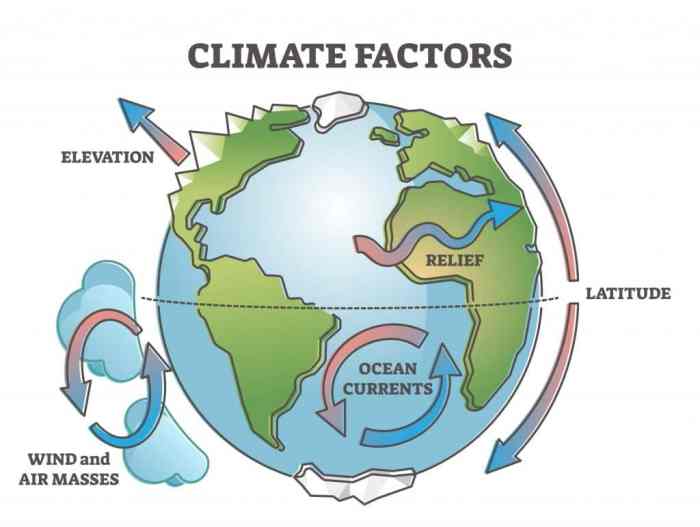
Section 21.1 explores the diverse factors that influence the Earth’s climate, shaping its patterns and variability. Understanding these factors is crucial for comprehending the mechanisms driving climate change and its potential impacts.
Natural Factors that Affect Climate
Natural factors play a significant role in determining climate patterns. These include:
- Solar radiation:The amount of solar energy reaching the Earth’s surface drives temperature and precipitation patterns.
- Earth’s rotation:The rotation of the Earth on its axis creates the Coriolis effect, which influences ocean currents and wind patterns.
- Ocean currents:Warm and cold ocean currents transport heat around the globe, affecting regional climates.
Human-Induced Factors that Affect Climate
Human activities have significantly impacted the Earth’s climate in recent decades. Key factors include:
- Greenhouse gas emissions:Burning fossil fuels releases carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, trapping heat and contributing to global warming.
- Deforestation:Clearing forests reduces the Earth’s ability to absorb carbon dioxide and regulate temperatures.
- Urbanization:Urban areas release heat and air pollutants, creating urban heat islands and altering local climate patterns.
Feedback Mechanisms in Climate Systems
Climate systems exhibit feedback mechanisms that can amplify or dampen climate change. Positive feedback mechanisms, such as melting ice releasing more greenhouse gases, accelerate warming, while negative feedback mechanisms, such as increased cloud cover reflecting solar radiation, can slow warming.
Climate Variability and Climate Change

Climate variability refers to short-term fluctuations in climate, while climate change refers to long-term shifts in average climate conditions. Natural and human-induced factors contribute to both climate variability and climate change.
Climate Models and Projections

Climate models are computer simulations that predict future climate based on historical data and scientific understanding. While models are essential for understanding climate change, they have uncertainties and limitations that need to be considered.
Climate Change Impacts and Adaptation: Section 21.1 Factors That Affect Climate Answer Key
Climate change poses significant risks to ecosystems, human societies, and the economy. Impacts include sea-level rise, extreme weather events, and changes in biodiversity. Adaptation strategies are crucial for mitigating the negative effects of climate change.
Answers to Common Questions
What are the key natural factors that influence climate?
Solar radiation, Earth’s rotation, ocean currents, and atmospheric circulation play significant roles in shaping climate patterns.
How do human activities contribute to climate change?
Greenhouse gas emissions from fossil fuel combustion, deforestation, and urbanization are primary human-induced factors driving climate change.
What is the difference between climate variability and climate change?
Climate variability refers to short-term fluctuations in climate patterns, while climate change encompasses long-term shifts in these patterns due to natural or human-induced factors.